Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent


Die Casting vs Others: What’s Trending in 2024
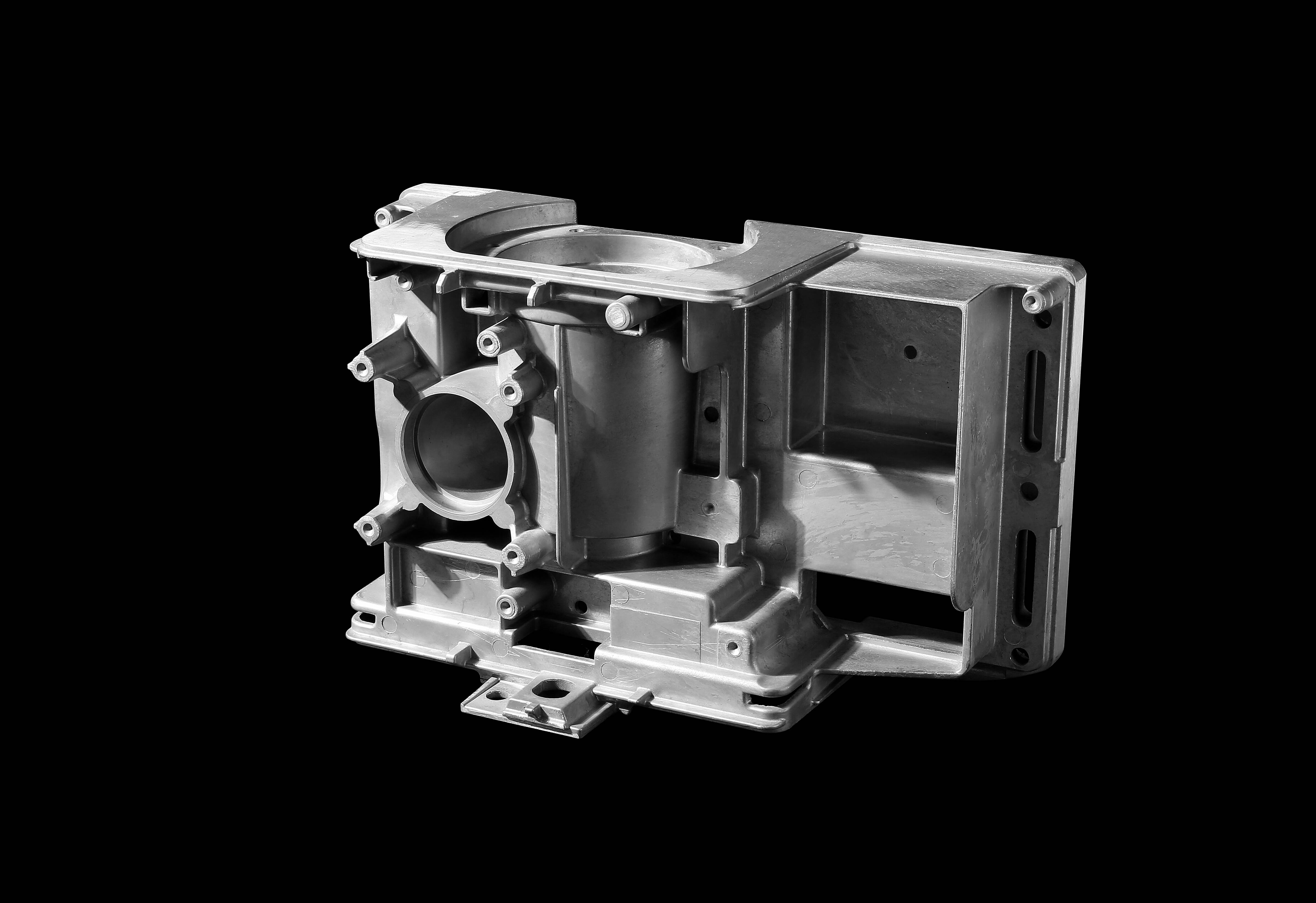
Die casting has revolutionized manufacturing by delivering unmatched precision and efficiency. This process forces molten metal into molds under high pressure, creating intricate parts with exceptional dimensional accuracy. Industries like automotive, electronics, and aerospace rely on it for producing components at scale. In 2024, advancements in technology are pushing die casting to new heights. You can expect faster production cycles, eco-friendly practices, and innovations tailored to industry needs. Its ability to produce complex shapes with minimal waste makes it a standout choice compared to other methods like CNC machining or sand casting.
Key Takeaways
-
Die casting offers unmatched precision and efficiency, making it ideal for high-volume production in industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
-
The process allows for the creation of complex shapes with minimal waste, providing significant cost savings and environmental benefits.
-
Advancements in technology, such as automation and AI, are enhancing die casting's speed and quality, making it a more reliable manufacturing choice.
-
Sustainability is becoming a priority, with manufacturers adopting eco-friendly practices and using recycled materials to reduce environmental impact.
-
Die casting is more cost-effective than CNC machining for large-scale production, while CNC machining is better suited for customization and small batches.
-
For metal parts requiring strength and precision, die casting is preferred over injection molding, which is better for lightweight plastic products.
-
Understanding the differences between die casting and other methods like sand casting and 3D printing can help you choose the right process for your manufacturing needs.
Overview of Die Casting
What is Die Casting?
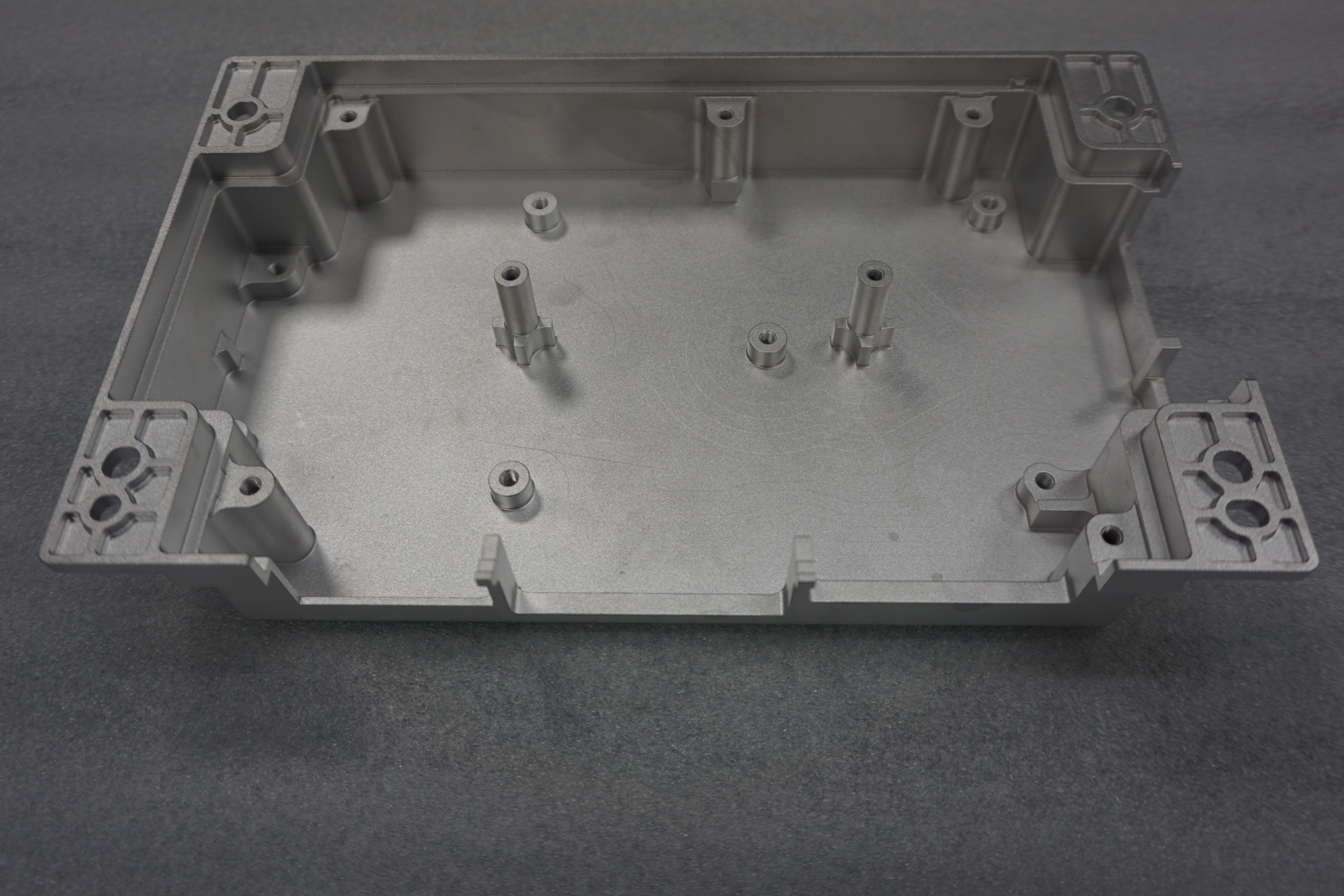
Die casting is a manufacturing process that uses high pressure to inject molten metal into a reusable steel mold, known as a die. This method creates metal parts with exceptional precision and intricate details. The process works efficiently for non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. By using advanced machinery, die casting achieves rapid production cycles, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
The technique has evolved significantly since its invention in the 19th century. Today, it is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, offering unmatched accuracy and reliability. Industries rely on die casting to produce components with tight tolerances and excellent surface finishes. Its ability to create complex shapes with minimal material waste sets it apart from other methods.
Key Advantages of Die Casting
Die casting offers several benefits that make it a preferred choice for manufacturers:
-
High Precision: The process delivers parts with excellent dimensional accuracy, ensuring consistency across large production runs.
-
Complex Geometry: Die casting allows the creation of intricate shapes and thin-walled sections that other methods struggle to achieve.
-
Smooth Surface Finish: Components produced through die casting often require little to no post-processing, saving time and costs.
-
Material Versatility: It supports a wide range of non-ferrous metals, including aluminum and zinc, which provide strength and durability.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: The reusability of molds and high-speed production cycles reduce per-unit costs, especially for large quantities.
-
Enhanced Mechanical Properties: Parts produced through die casting exhibit excellent strength-to-weight ratios, making them suitable for demanding applications.
These advantages make die casting an efficient and reliable solution for producing high-quality metal parts.
Common Applications of Die Casting
Die casting plays a vital role in various industries due to its versatility and efficiency. Some common applications include:
-
Automotive Industry: Manufacturers use die casting to produce engine blocks, transmission cases, and structural components. These parts require strength, precision, and lightweight properties.
-
Aerospace Sector: The process creates lightweight yet durable components like brackets and housings, essential for aircraft performance.
-
Electronics: Die casting produces intricate parts such as connectors, heat sinks, and enclosures, ensuring reliability in electronic devices.
-
Consumer Goods: Items like kitchen appliances, power tools, and decorative hardware benefit from the smooth finishes and complex designs achievable through die casting.
By meeting the demands of these industries, die casting continues to be a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
Die Casting vs Other Manufacturing Processes
Die Casting vs CNC Machining
When comparing die casting to CNC machining, you notice significant differences in their applications and benefits. Die casting excels in high-volume production. It uses molds to create parts quickly and efficiently, making it ideal for industries that require large quantities of components. CNC machining, on the other hand, focuses on precision and customization. It removes material from a solid block to shape the desired part, which works well for prototypes or low-volume production.
Die casting offers faster production cycles and reduces material waste. The process injects molten metal into reusable molds, ensuring consistency across all parts. CNC machining, however, allows for greater flexibility. You can modify designs easily without creating new molds, which is especially useful during the development phase of a product.
Key Insight: Die casting is more cost-effective for large-scale manufacturing, while CNC machining suits projects requiring customization or small batches.
Die Casting vs Injection Molding
Die casting and injection molding share similarities, as both involve injecting material into molds. However, the materials they use and their applications differ. Die casting works with metals like aluminum and zinc, producing durable and strong components. Injection molding, in contrast, uses plastics, making it suitable for lightweight and less rigid products.
Die casting provides excellent dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finishes. This makes it a preferred choice for industries like automotive and aerospace, where strength and precision are critical. Injection molding, while versatile, cannot match the durability of metal parts. However, it shines in producing lightweight items such as packaging, toys, and consumer goods.
Key Insight: Choose die casting for metal parts requiring strength and precision. Opt for injection molding when working with plastics or lightweight materials.
Die Casting vs 3D Printing
Die casting and 3D printing represent two distinct approaches to manufacturing. Die casting focuses on speed and efficiency for high-volume production. It uses molds to create parts with consistent quality and minimal waste. 3D printing, however, emphasizes design flexibility. It builds parts layer by layer, allowing for intricate and complex geometries.
For large-scale production, die casting proves more cost-effective. The reusability of molds and rapid production cycles lower per-unit costs. 3D printing, though slower, eliminates the need for molds. This reduces lead times and tooling expenses, making it ideal for prototyping or custom designs.
Key Insight: Die casting is the go-to method for mass production of metal parts. 3D printing excels in creating unique, complex designs or prototypes.
Die Casting vs Sand Casting
Die casting and sand casting are two popular methods for producing metal parts, but they differ significantly in their processes, applications, and benefits. Understanding these differences can help you choose the right method for your manufacturing needs.
Die casting uses high pressure to inject molten metal into a reusable steel mold, creating parts with exceptional precision and smooth surface finishes. Sand casting, on the other hand, involves pouring molten metal into a sand-based mold, which is destroyed after each use. This fundamental difference impacts the efficiency, quality, and cost of production.
Here’s how the two methods compare:
-
Precision and Surface Finish: Die casting delivers parts with tight tolerances and excellent surface finishes. Sand casting, while versatile, often results in rougher surfaces and less dimensional accuracy. If your project demands intricate details and smooth finishes, die casting is the superior choice.
-
Production Speed: Die casting excels in high-volume production due to its rapid cycle times and reusable molds. Sand casting requires more time to prepare molds for each part, making it less efficient for large-scale manufacturing.
-
Material Waste: Die casting minimizes material waste by using precise molds and controlled processes. Sand casting generates more waste, as the molds are single-use and often require additional finishing work.
-
Cost Efficiency: For large production runs, die casting proves more cost-effective. The reusability of molds and faster production cycles reduce per-unit costs. Sand casting, however, is better suited for low-volume production or projects requiring larger, simpler parts.
-
Applications: Die casting is ideal for industries like automotive and electronics, where precision and consistency are critical. Sand casting works well for producing large components, such as engine blocks or heavy machinery parts, where surface finish and tight tolerances are less important.
Key Insight: Choose die casting for high-volume production of intricate, high-quality parts. Opt for sand casting when working on low-volume projects or producing large, simple components.
By understanding these differences, you can make informed decisions that align with your manufacturing goals.
Trends in Die Casting and Manufacturing for 2024
Advancements in Die Casting Technology
In 2024, technological advancements are transforming die casting into an even more efficient and precise manufacturing process. Modern machinery now integrates automation and artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize production cycles. These innovations allow you to achieve faster turnaround times while maintaining exceptional quality. For instance, AI-powered systems can monitor and adjust parameters in real-time, ensuring consistent results across every batch.
Another breakthrough is the development of enhanced mold materials. These materials improve durability and heat resistance, enabling longer mold lifespans and reducing downtime. You can also benefit from innovations like vacuum-assisted die casting, which minimizes porosity and enhances the mechanical properties of components. These advancements make die casting a more reliable choice for industries requiring high-performance parts.
Key Insight: By adopting cutting-edge technology, you can produce intricate components with greater speed and precision, meeting the demands of modern manufacturing.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Practices
Sustainability is a growing priority in manufacturing, and die casting is no exception. In 2024, eco-friendly practices are reshaping the industry. Manufacturers are now focusing on reducing energy consumption by using energy-efficient furnaces and recycling excess materials. This not only lowers production costs but also minimizes environmental impact.
You can also see a shift toward using sustainable alloys. Recycled aluminum and zinc are becoming popular choices, as they retain their properties while reducing the need for raw materials. Additionally, advancements in mold design are helping to reduce material waste. By optimizing mold geometry, manufacturers can produce parts with minimal scrap, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Key Insight: Embracing eco-friendly practices in die casting helps you meet environmental standards while maintaining cost efficiency and product quality.
Industry-Specific Innovations
Die casting continues to evolve with innovations tailored to specific industries. In the automotive sector, lightweighting remains a top priority. Manufacturers are leveraging die casting to produce thinner, stronger components that improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions. For example, aluminum die casting is widely used to create lightweight engine blocks and structural parts.
In the aerospace industry, the focus is on precision and durability. Die casting enables you to produce complex geometries with tight tolerances, essential for aircraft performance. Meanwhile, the electronics sector benefits from advancements in miniaturization. Die casting now supports the production of smaller, more intricate components like heat sinks and connectors, ensuring reliability in compact devices.
Key Insight: Industry-specific innovations in die casting allow you to address unique challenges, from lightweight automotive parts to high-precision aerospace components.
Die casting continues to lead as a manufacturing process due to its unmatched precision and efficiency. You can rely on it for high-volume production, especially in industries like automotive, electronics, and aerospace. Its ability to produce intricate parts with minimal waste makes it a preferred choice over other methods. In 2024, advancements like automation, eco-friendly practices, and industry-specific innovations are reshaping the landscape. By adopting these trends, you can achieve scalable, high-quality production while staying ahead in a competitive market.
FAQ
What makes die casting a cost-effective manufacturing process?
Die casting stands out as one of the most cost-effective methods for high-volume production. It uses reusable molds, which significantly reduce per-unit costs when producing large quantities. The process also minimizes material waste and requires little to no post-processing, saving both time and resources. Its ability to produce hundreds of thousands of precise parts quickly makes it an economical choice for manufacturers.
Key Insight: Die casting combines speed, precision, and scalability, making it ideal for mass production with reduced costs.
How does die casting achieve such high precision?
Die casting uses high-pressure injection to fill molds, ensuring every detail of the mold is captured. This results in parts with tight dimensional tolerances and excellent surface finishes. The process also allows for the creation of intricate geometries that other methods struggle to replicate. This precision makes die casting suitable for industries requiring consistent and accurate components.
Fact: Die casting delivers exceptional accuracy, reducing the need for secondary machining operations.
What materials can you use in die casting?
Die casting primarily works with non-ferrous metals like aluminum, zinc, magnesium, and copper. These materials offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios, durability, and corrosion resistance. Aluminum and zinc are particularly popular due to their versatility and ability to produce lightweight yet strong components.
Tip: Choose the material based on your project’s requirements for strength, weight, and durability.
Why is die casting preferred for high-volume production?
Die casting excels in high-volume production because of its rapid cycle times and reusable molds. The process allows you to produce identical parts consistently and efficiently. This makes it a preferred choice for industries like automotive and electronics, where large quantities of components are needed.
Key Advantage: Die casting reduces production time and costs, making it ideal for large-scale manufacturing.
How does die casting compare to sand casting?
Die casting offers better precision, smoother surface finishes, and faster production speeds compared to sand casting. While sand casting is more flexible for producing large, simple parts, die casting is better suited for intricate designs and high-volume applications. The reusability of molds in die casting also makes it more cost-effective for mass production.
Comparison: Use die casting for precision and speed. Opt for sand casting for low-volume or large-scale parts.
Can die casting produce complex shapes?
Yes, die casting is highly effective for creating complex shapes. The high-pressure injection process ensures that molten metal fills every detail of the mold, allowing for intricate geometries and thin-walled sections. This capability makes it a go-to method for industries requiring detailed and precise components.
Fact: Die casting achieves shapes and tolerances that are difficult to replicate with other manufacturing methods.
Is die casting environmentally friendly?
Die casting has become more eco-friendly with advancements in technology. Manufacturers now use energy-efficient furnaces and recycle excess materials to reduce waste. Sustainable alloys, such as recycled aluminum and zinc, are also gaining popularity. These practices align with global sustainability goals while maintaining production efficiency.
Tip: Adopting eco-friendly die casting practices helps you meet environmental standards without compromising quality.
What industries benefit the most from die casting?
Die casting serves a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods. In the automotive sector, it produces lightweight engine blocks and structural components. Aerospace relies on it for precision parts, while electronics benefit from intricate components like heat sinks and connectors.
Key Insight: Die casting’s versatility makes it indispensable across multiple industries.
How does die casting compare to 3D printing?
Die casting is faster and more cost-effective for high-volume production. It uses reusable molds to produce consistent parts with minimal waste. 3D printing, on the other hand, excels in design flexibility and prototyping. While 3D printing eliminates the need for molds, it cannot match die casting’s speed and efficiency for mass production.
Comparison: Choose die casting for large-scale manufacturing. Use 3D printing for custom designs or prototypes.
What are the key trends in die casting for 2024?
In 2024, automation and artificial intelligence are revolutionizing die casting. These technologies optimize production cycles and improve quality control. Sustainability is another major trend, with manufacturers focusing on energy efficiency and recycled materials. Industry-specific innovations, such as lightweighting in automotive and miniaturization in electronics, are also shaping the future of die casting.
Future Outlook: Embracing these trends will help you stay competitive and meet evolving market demands.